Cooking gas, primarily consisting of propane and butane, is produced through various methods such as natural gas extraction, refining of crude oil, or by processing organic materials. This gas is essential for cooking and heating in homes and industries.
How cooking gas is produced
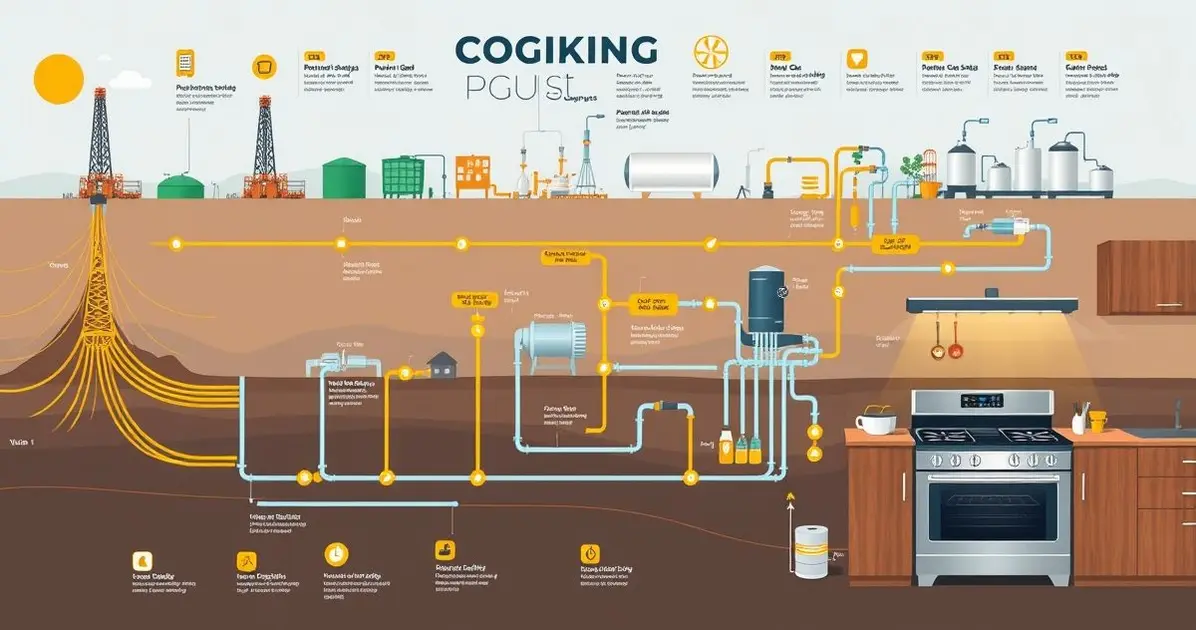
Cooking gas is produced by refining natural gas and crude oil or through biogas processes. The gas is extracted, purified, and compressed for distribution, making it an essential energy source for cooking and heating in households worldwide.
Extraction of Hydrocarbons from Natural Gas and Crude Oil
The extraction of hydrocarbons from natural gas and crude oil is the foundational step in the production of cooking gas. This process involves several techniques to obtain the raw materials necessary for creating liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Here’s a detailed look at how hydrocarbons are extracted:
1. Natural Gas Extraction: Natural gas is primarily composed of methane and is found in underground reservoirs. The extraction process typically involves:
- Drilling: Wells are drilled into the earth to reach gas reservoirs. This can be done through vertical drilling, where a well is drilled straight down to access the gas pocket, or through horizontal drilling, which allows for greater access to gas deposits within the rock formation.
- Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking): In cases where natural gas is trapped in shale formations, hydraulic fracturing is employed. This process involves injecting high-pressure fluid into the rock to create fractures, allowing the gas to flow more freely to the surface.
2. Crude Oil Extraction: Crude oil is another significant source of hydrocarbons for LPG production. The extraction process for crude oil includes:
- Conventional Drilling: Similar to natural gas extraction, conventional drilling involves drilling wells into oil reservoirs. The pressure within the reservoir allows the oil to flow to the surface once the well is opened.
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): In mature oil fields where pressure has decreased, enhanced oil recovery techniques may be used to extract additional oil. This can involve injecting water, steam, or gas into the reservoir to increase pressure and facilitate oil flow.
3. Collection and Transportation: Once extracted, the hydrocarbons are collected and transported to processing facilities. This may involve pipelines or tanker trucks, depending on the location of the extraction site and the processing facility.
In summary, the extraction of hydrocarbons from natural gas and crude oil is a complex process that employs various drilling techniques and technologies. Understanding these extraction methods is essential for appreciating the production of cooking gas and the energy resources that power our daily lives.
Refining Techniques for Separating Propane and Butane
Refining techniques for separating propane and butane are critical steps in the production of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). These techniques ensure that the hydrocarbons are effectively separated and purified for safe use in cooking and heating. Here’s a detailed overview of the key refining methods used for this separation:
1. Fractional Distillation: Fractional distillation is the primary method used to separate propane and butane from crude oil and natural gas liquids. This process involves:
- Heating the Mixture: The crude oil or natural gas liquids are heated in a distillation column. As the mixture heats up, different components vaporize at different temperatures based on their boiling points.
- Separation of Components: As the vapors rise through the distillation column, they cool and condense at various levels. Propane and butane have specific boiling points (propane at approximately -42°C and butane at about -0.5°C), allowing them to be collected separately as they condense at different heights in the column.
- Collection: The separated propane and butane are collected in different containers for further processing, ensuring that they meet the required purity standards.
2. Gas Processing Plants: In gas processing plants, additional refining techniques may be employed to further purify propane and butane:
- Absorption: In this method, natural gas is passed through a liquid absorbent that selectively absorbs heavier hydrocarbons like propane and butane, allowing lighter gases like methane to pass through. The absorbed hydrocarbons are then stripped from the absorbent for further refinement.
- Adsorption: Similar to absorption, adsorption uses solid materials to capture and separate propane and butane from the gas mixture. This method can enhance the purity of the separated gases.
3. Purification Processes: After separation, additional purification processes are often employed to remove any remaining impurities:
- Dehydration: This process removes water vapor from the separated propane and butane, which is essential for preventing corrosion and ensuring safe storage.
- Filtration: Filtration techniques may be used to remove any solid particles or contaminants that could affect the quality of the LPG.
In summary, refining techniques for separating propane and butane are essential for producing high-quality liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Through methods such as fractional distillation, absorption, and additional purification processes, these hydrocarbons are effectively separated and refined for safe use in cooking and heating applications. Understanding these techniques highlights the complexity of gas production and the importance of quality control in ensuring a reliable energy source.

Environmental Considerations in Cooking Gas Production
Environmental considerations in cooking gas production are crucial for ensuring that the processes involved are sustainable and minimize negative impacts on the planet. As the demand for cooking gas increases, it is essential to address the environmental implications associated with its extraction and production. Here are the key environmental considerations:
1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The extraction and processing of natural gas and crude oil can result in significant greenhouse gas emissions. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, can be released during drilling, extraction, and transportation. Mitigating these emissions is vital for reducing the overall carbon footprint of cooking gas production.
2. Water Usage and Contamination: Hydraulic fracturing (fracking), used in unconventional natural gas extraction, requires substantial amounts of water. This can lead to water scarcity in certain regions. Additionally, there is a risk of water contamination from chemicals used in the fracking process, which can affect local water supplies and ecosystems.
3. Habitat Disruption: The construction of drilling sites, pipelines, and processing facilities can disrupt local habitats and wildlife. It is essential to conduct environmental impact assessments before initiating extraction projects to minimize habitat destruction and protect biodiversity.
4. Waste Management: The production of cooking gas generates waste, including drilling muds and other byproducts. Proper waste management practices are crucial to prevent pollution and ensure that waste is handled responsibly. This includes recycling and disposing of waste materials in an environmentally friendly manner.
5. Sustainable Practices: Implementing sustainable practices in cooking gas production can help mitigate environmental impacts. This includes investing in technologies that reduce emissions, improving energy efficiency, and utilizing renewable energy sources in the production process.
6. Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities affected by gas extraction and production is essential for addressing environmental concerns. Transparent communication and collaboration can help ensure that community needs are considered and that responsible practices are implemented.
In summary, environmental considerations in cooking gas production are critical for promoting sustainability and minimizing negative impacts on the environment. By addressing greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, habitat disruption, and waste management, the cooking gas industry can work towards a more sustainable future while meeting the energy needs of households and businesses.
Safety Measures and Efficiency in Modern Production
Safety measures and efficiency in modern cooking gas production are essential components that ensure the safe handling and processing of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and natural gas. As the demand for cooking gas continues to grow, the industry has implemented various strategies to enhance safety and operational efficiency. Here’s an overview of the key safety measures and efficiency practices in modern production:
1. Advanced Safety Protocols: The safety of workers and consumers is paramount in cooking gas production. Modern facilities adhere to strict safety protocols, including:
- Regular Safety Training: Employees undergo comprehensive safety training to familiarize themselves with emergency procedures, equipment handling, and hazard recognition.
- Leak Detection Systems: Advanced technology is employed to detect gas leaks promptly. These systems utilize sensors and monitoring equipment to identify leaks in real-time, allowing for immediate action to prevent accidents.
- Emergency Preparedness Plans: Facilities must have emergency response plans in place to address potential incidents, such as explosions or leaks. These plans include evacuation routes, communication strategies, and coordination with local emergency services.
2. Efficient Production Techniques: Modern cooking gas production facilities utilize efficient techniques to maximize output while minimizing waste and environmental impact:
- Automation and Technology: Automation in the production process enhances efficiency and reduces human error. Advanced technologies streamline operations, from extraction to refining, ensuring consistent quality and safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Many facilities are adopting energy-efficient practices, such as using waste heat recovery systems and optimizing energy consumption during production. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the carbon footprint.
- Process Optimization: Continuous improvement methodologies, such as Lean and Six Sigma, are applied to refine processes and eliminate inefficiencies. This leads to better resource management and increased productivity.
3. Environmental Compliance: Modern production facilities are required to comply with environmental regulations to minimize their impact on the environment:
- Emission Controls: Facilities implement technologies to control emissions and reduce the release of greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Waste Management Practices: Proper waste management is essential to prevent environmental contamination. Facilities are required to manage byproducts responsibly, including recycling and safe disposal methods.
In summary, safety measures and efficiency in modern cooking gas production are vital for ensuring the safe handling of LPG and natural gas. By implementing advanced safety protocols, optimizing production techniques, and adhering to environmental regulations, the industry can provide a reliable energy source while prioritizing safety and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the production of cooking gas involves a complex interplay of safety measures and efficiency practices that are crucial for delivering a reliable and safe energy source.
From the extraction of hydrocarbons to the refining processes that produce liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), each step is designed to ensure the highest standards of safety and quality.
Modern facilities employ advanced technologies and rigorous safety protocols to protect both workers and consumers. The implementation of leak detection systems, regular safety training, and emergency preparedness plans reflects the industry’s commitment to safety in cooking gas production.
Moreover, the focus on efficiency through automation, energy optimization, and process improvement not only enhances productivity but also reduces environmental impact. By adhering to strict environmental compliance measures, the industry can minimize emissions and promote sustainable practices.
Understanding the significance of these safety measures and efficiency practices empowers consumers to appreciate the complexities behind the cooking gas they use daily. As we continue to rely on cooking gas as a primary energy source, it is essential to support practices that prioritize safety, sustainability, and responsible resource management for a cleaner and safer future.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Cooking Gas Production
How is cooking gas produced?
Cooking gas is produced through the extraction of hydrocarbons from natural gas and crude oil, followed by refining processes that convert these raw materials into liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
What extraction methods are used for natural gas?
Natural gas is extracted using conventional drilling and unconventional methods such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling.
What refining techniques are involved in LPG production?
Key refining techniques include fractional distillation, where different hydrocarbons are separated based on boiling points, and purification processes to remove impurities.
What safety measures are implemented in cooking gas production?
Safety measures include regular safety training for employees, leak detection systems, emergency preparedness plans, and compliance with safety regulations.
How does cooking gas production impact the environment?
Cooking gas production can lead to greenhouse gas emissions and water contamination if not managed properly. However, LPG is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to other fossil fuels.
What are the benefits of using cooking gas?
Cooking gas is efficient, provides a consistent heat source, and is cleaner-burning than many other fossil fuels, making it a popular choice for cooking and heating.
See more
Discover plenty of easy and delicious recipes you can make at home, from hearty dinners to indulgent desserts and wholesome breakfasts.




