Cooking gas, primarily made from natural gas, undergoes a detailed production process that involves extraction, refinement, and distribution. Understanding this process helps us appreciate the essential fuel that powers our kitchens.
How cooking gas is made
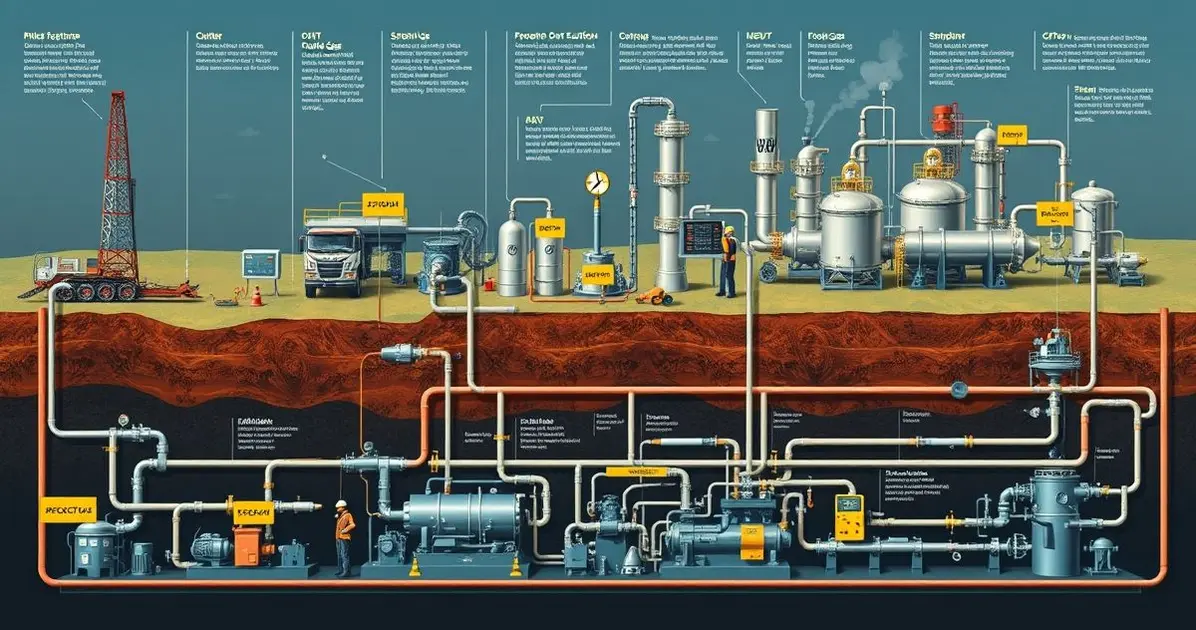
The manufacturing of cooking gas starts with the extraction of natural gas from underground sources. Afterward, the gas is purified and processed, removing impurities before being transported to homes. This essential fuel is vital for cooking and heating.
Raw Materials for Cooking Gas Production
The production of cooking gas primarily relies on two key raw materials: natural gas and crude oil. Understanding these materials is essential for grasping how cooking gas is made.
1. Natural Gas: Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is primarily composed of methane (CH4), a highly combustible hydrocarbon. It is found deep beneath the earth’s surface, often in association with other fossil fuels like oil. Natural gas is extracted through drilling and is a significant source of energy for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Its clean-burning properties make it an environmentally friendly choice compared to other fossil fuels.
2. Crude Oil: Crude oil is another vital raw material used in the production of cooking gas, particularly liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons that is extracted from the earth through drilling. Crude oil undergoes refining processes to separate its various components, including propane and butane, which are key constituents of LPG used for cooking. The refining process involves heating the crude oil and using fractional distillation to separate the hydrocarbons based on their boiling points.
3. Additional Components: In addition to methane from natural gas and hydrocarbons from crude oil, other components may also be involved in the production process. These can include ethane, butane, and propane, which can be extracted or separated during the refining process and used in various applications, including cooking gas.
In summary, the raw materials for cooking gas production include natural gas and crude oil, both of which undergo extraction and refining processes to produce the gas that powers our kitchens. Understanding these materials is crucial for appreciating the complexities of cooking gas production and its impact on energy consumption.
Natural Gas Extraction and Refining Processes
The extraction and refining processes of natural gas are critical steps in producing cooking gas. Understanding these processes helps illuminate how raw natural gas is transformed into a usable energy source for cooking and heating.
1. Extraction of Natural Gas: Natural gas is extracted from underground reservoirs using various drilling techniques. The two primary methods of extraction are:
- Conventional Drilling: This method involves drilling vertical wells into gas reservoirs located in porous rock formations. Once the well reaches the gas pocket, the pressure allows the gas to flow to the surface.
- Unconventional Extraction: Techniques such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling are used to extract natural gas from shale formations and other tight rock layers. Fracking involves injecting high-pressure water mixed with sand and chemicals into the rock to create fractures, allowing gas to escape.
2. Initial Processing: Once natural gas is extracted, it undergoes initial processing to remove impurities and separate it from other hydrocarbons. This step typically includes:
- Separation: The extracted gas is passed through separators to remove liquids, such as water, oil, and condensates. This helps ensure that the gas is in its purest form before further processing.
- Removal of Impurities: Additional treatments may be employed to remove sulfur compounds, carbon dioxide, and other contaminants that can affect the quality of the gas.
3. Refining Processes: After initial processing, natural gas undergoes refining to enhance its quality and prepare it for distribution. Key refining processes include:
- Fractional Distillation: This process separates natural gas into its various components based on boiling points. Methane, ethane, propane, and butane can be extracted during this process, allowing for the production of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and other products.
- Purification: Further purification techniques, such as amine gas treating, may be used to remove remaining impurities and ensure that the gas meets safety and quality standards.
4. Compression and Storage: After refining, the natural gas is compressed for transportation through pipelines. Compression reduces the volume of the gas, making it more efficient to transport. The gas is then stored in large underground reservoirs or tanks until it is needed for distribution.
In summary, the extraction and refining processes of natural gas are essential for producing clean and efficient cooking gas. By understanding these processes, we can appreciate the complexity and technology involved in delivering this vital energy source to our homes.

Transformation of Crude Oil into LPG
The transformation of crude oil into liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a critical process in the production of cooking gas. This process involves several steps that convert raw crude oil into usable fuel for cooking and heating. Here’s a detailed look at how this transformation occurs:
1. Extraction of Crude Oil: The journey begins with the extraction of crude oil from underground reservoirs. This is done through drilling wells, where the oil is pumped to the surface. Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and other organic materials, and it serves as the primary raw material for producing LPG.
2. Refining Process: Once extracted, crude oil undergoes a refining process to separate its components. This is typically achieved through fractional distillation, a method that utilizes heat to separate the various hydrocarbons based on their boiling points:
- Fractional Distillation: In this process, crude oil is heated in a distillation column. As the oil heats up, different components vaporize at different temperatures. The vapors rise through the column and are condensed back into liquid form at various levels, allowing for the collection of different fractions, including LPG.
3. Collection of LPG: During fractional distillation, propane and butane are separated from other lighter and heavier hydrocarbons. These gases are collected and further processed to ensure they meet safety and quality standards. LPG is composed primarily of propane and butane, making it an efficient fuel source.
4. Purification: After collection, LPG undergoes purification to remove any remaining impurities, such as sulfur compounds and other contaminants. This step is crucial to ensure that the LPG is safe and suitable for use in cooking and heating applications.
5. Compression and Liquefaction: Once purified, propane and butane are compressed and cooled to transform them into a liquid state. This liquefaction process makes it easier to store and transport LPG, as it occupies significantly less volume in its liquid form compared to its gaseous state.
6. Storage and Distribution: The liquefied petroleum gas is then stored in pressurized tanks or cylinders, ready for distribution to consumers. LPG is commonly delivered to households and businesses for use in cooking, heating, and hot water systems.
In summary, the transformation of crude oil into LPG involves a series of steps, including extraction, refining, purification, and liquefaction. This process is essential for producing the cooking gas that many households rely on, highlighting the complexity and technology behind this vital energy source.
Safety Standards and Environmental Considerations
Safety standards and environmental considerations play a crucial role in the production and handling of cooking gas, particularly liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Ensuring that these standards are met is essential for protecting both human health and the environment. Here’s an overview of the key aspects:
1. Safety Standards in Production: The production of cooking gas is governed by strict safety regulations designed to prevent accidents and ensure safe handling. These standards include:
- Quality Control: LPG production facilities must adhere to rigorous quality control measures, ensuring that the gas produced meets specific safety and purity standards.
- Equipment Safety: All equipment used in the extraction, refining, and distribution of LPG must be regularly inspected and maintained to prevent leaks, malfunctions, and accidents.
- Training and Certification: Personnel involved in the production and handling of LPG must undergo training and certification to ensure they are knowledgeable about safety protocols and emergency procedures.
2. Environmental Considerations: The production and use of cooking gas also have environmental implications that must be addressed:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: LPG is considered a cleaner-burning fuel compared to other fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. Its use can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more environmentally friendly option for cooking and heating.
- Minimizing Air Pollution: Adhering to environmental regulations during the production process helps minimize air pollution from harmful emissions. This includes controlling the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants that can impact air quality.
- Waste Management: Proper waste management practices must be implemented to handle any byproducts or waste generated during the production process. This includes recycling and responsible disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination.
3. Emergency Preparedness: Facilities involved in LPG production and distribution must have emergency response plans in place to address potential accidents, such as leaks or explosions. These plans should include evacuation procedures, communication strategies, and coordination with local emergency services.
In summary, safety standards and environmental considerations are vital components of the cooking gas production process. By adhering to these standards, the industry can ensure the safe handling of LPG while minimizing its environmental impact, ultimately contributing to a safer and more sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how cooking gas is made, from the extraction of raw materials to the transformation of crude oil into liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is essential for appreciating its role in our daily lives.
The production process involves several key steps, including natural gas extraction, refining, and purification, each of which is governed by strict safety standards to ensure the well-being of both workers and consumers.
Moreover, environmental considerations are critical in the production of cooking gas. By adhering to safety protocols and minimizing emissions, the industry can reduce its impact on the environment while providing a cleaner-burning fuel option for cooking and heating.
As consumers, being informed about the journey of cooking gas and the importance of safety and environmental standards empowers us to make better choices. Whether it’s through supporting companies that prioritize sustainability or understanding the benefits of cleaner fuels, we can all play a part in promoting a safer and greener future.
Ultimately, the journey of cooking gas reflects the intersection of technology, safety, and environmental responsibility, highlighting the importance of innovation in creating sustainable energy solutions.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Cooking Gas Production
How is cooking gas made?
Cooking gas is produced through the extraction of natural gas and crude oil, followed by refining processes that convert these raw materials into liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
What raw materials are used in cooking gas production?
The primary raw materials for cooking gas production are natural gas and crude oil, which are extracted and processed to create LPG.
What are the main steps in the production process of cooking gas?
The main steps include extraction, initial processing, refining, and transformation into LPG, followed by storage and distribution.
What safety standards are in place for cooking gas production?
Safety standards include quality control measures, equipment safety inspections, personnel training, and emergency preparedness plans.
What are the environmental benefits of using cooking gas?
Cooking gas is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to other fossil fuels, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
How can I ensure the safe use of cooking gas in my home?
Ensure proper ventilation, regularly check for leaks, follow manufacturer instructions, and keep gas appliances well-maintained to ensure safe use.
See more
Discover plenty of easy and delicious recipes you can make at home, from hearty dinners to indulgent desserts and wholesome breakfasts.




