Refining cooking oil is a critical process that enhances its quality and shelf life. This involves several stages, each aimed at removing impurities and ensuring the oil is safe and suitable for consumption.
How cooking oil is refined
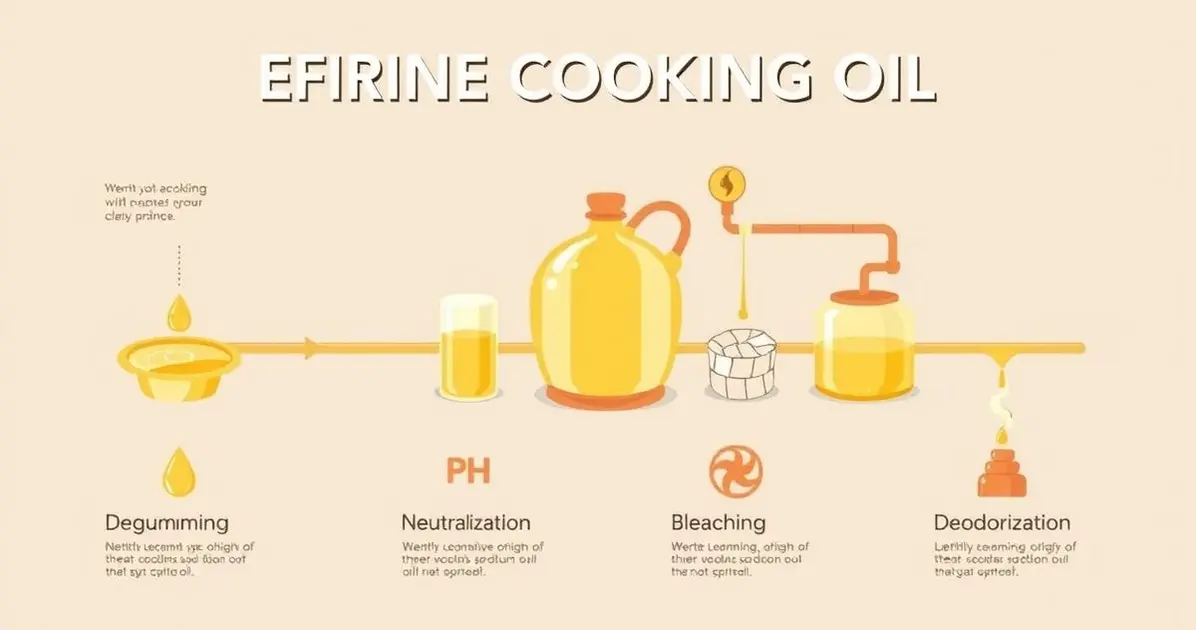
The refining of cooking oil involves multiple steps: degumming removes phospholipids, neutralization eliminates free fatty acids, bleaching clears color, and deodorization removes odors. This process results in clear, tasteless oil that is ideal for cooking.
Extraction of Raw Plant Sources
The extraction of raw plant sources is the first crucial step in the production of cooking oil. This process involves obtaining oil from various seeds, nuts, and fruits, and it can be accomplished through two primary methods: mechanical pressing and solvent extraction.
1. Mechanical Pressing: This traditional method involves physically squeezing the oil from the plant material using mechanical presses. It is often preferred for high-quality oils, such as olive oil and avocado oil, where minimal processing is desired to retain flavor and nutrients. The mechanical pressing process typically includes the following steps:
- Preparation: The seeds or fruits are cleaned and sometimes roasted to enhance flavor before pressing.
- Pressing: The prepared material is placed into a mechanical press, which applies pressure to extract the oil. The resulting oil is often referred to as “cold-pressed” when no additional heat is applied during extraction.
- Separation: After pressing, the oil is separated from the solid residue, known as cake or pomace, which can be used for animal feed or compost.
2. Solvent Extraction: This method is more commonly used for extracting oil from seeds with lower oil content, such as soybeans and canola. Solvent extraction is a more efficient process that typically yields a higher quantity of oil. The steps involved in solvent extraction include:
- Preparation: The seeds are cleaned and often ground into a meal to increase the surface area for extraction.
- Solvent Application: A solvent, usually hexane, is mixed with the seed meal. The solvent dissolves the oil, forming a mixture of oil and solvent.
- Separation: The oil-solvent mixture is then separated from the solid meal using a centrifuge or other separation methods. The solvent is then evaporated, leaving behind crude oil.
- Recovery of Solvent: The solvent is typically recovered and reused in the extraction process, making it a more sustainable method.
In summary, the extraction of raw plant sources is a vital step in cooking oil production. Whether through mechanical pressing or solvent extraction, this process determines the quality and yield of the oil. Understanding these extraction methods highlights the importance of sourcing quality ingredients for producing cooking oils that are both flavorful and nutritious.
Key Refinement Processes: Degumming and Neutralization
Once cooking oil is extracted from raw plant sources, it undergoes several key refinement processes to enhance its quality and safety. Two of the most important processes in this stage are degumming and neutralization.
1. Degumming: Degumming is the first step in the refining process and is crucial for removing impurities that can affect the oil’s quality. During extraction, natural oils contain phospholipids, proteins, and other impurities that can create cloudiness and affect flavor. The degumming process involves:
- Water Degumming: In this method, water is added to the crude oil, which helps to hydrate and separate the phospholipids from the oil. The hydrated phospholipids then form a sludge that can be easily removed by centrifugation.
- Acid Degumming: For oils with higher levels of impurities, acid degumming may be used. In this process, a mild acid (such as phosphoric acid) is added to the oil. The acid reacts with the impurities, allowing them to be separated and removed more effectively.
By removing these impurities, degumming improves the clarity and stability of the oil, making it more suitable for cooking and extending its shelf life.
2. Neutralization: The next key refinement process is neutralization, which involves removing free fatty acids from the oil. Free fatty acids can result from the breakdown of triglycerides during extraction and can negatively impact the flavor and shelf life of the oil. The neutralization process typically includes:
- Alkali Neutralization: In this method, an alkali solution, usually sodium hydroxide (lye), is added to the oil. The alkali reacts with the free fatty acids to form soap, which can then be separated from the oil. This effectively reduces the acidity of the oil and improves its taste.
- Washing: After neutralization, the oil may undergo a washing process to remove any remaining soap and impurities. This is done by adding warm water to the oil and then separating the water layer, which contains the soap and impurities.
In summary, degumming and neutralization are critical refinement processes that enhance the quality of cooking oil. By removing impurities and free fatty acids, these processes ensure that the oil is safe, stable, and suitable for culinary use. Understanding these key steps in the refining process highlights the importance of quality control in producing high-quality cooking oils.

Bleaching and Deodorization Techniques
After the initial refining processes of degumming and neutralization, cooking oil undergoes further treatment through bleaching and deodorization. These techniques are essential for improving the oil’s appearance, flavor, and stability. Here’s an overview of each process:
1. Bleaching: The bleaching process is designed to remove color pigments and impurities that can affect the visual appeal and quality of the oil. This step typically involves:
- Adsorption: During bleaching, the oil is treated with bleaching earth or activated carbon. These substances act as adsorbents, binding to color compounds, impurities, and any remaining traces of phospholipids. As the oil passes through the bleaching agent, the unwanted materials are removed, resulting in a lighter-colored oil.
- Temperature Control: The bleaching process often involves heating the oil to enhance the effectiveness of the adsorbents. The heat helps the bleaching agents work more efficiently, allowing for better removal of impurities.
By removing color and impurities, bleaching not only improves the oil’s appearance but also enhances its stability and shelf life.
2. Deodorization: Following bleaching, deodorization is carried out to eliminate any undesirable odors and flavors from the oil. This process is critical for ensuring that the oil has a neutral taste and aroma, making it suitable for various culinary applications. Deodorization typically involves:
- Steam Distillation: In this method, the oil is heated under a vacuum while steam is introduced. The steam carries away volatile compounds responsible for off-odors and flavors. This process is effective in removing unwanted smells without significantly affecting the oil’s quality.
- Temperature and Pressure Control: Deodorization is conducted at high temperatures and low pressures to maximize the removal of volatile compounds. This careful control ensures that the oil retains its desirable qualities while achieving a neutral aroma.
Overall, bleaching and deodorization are essential techniques in the refining process of cooking oil. By improving the oil’s color, flavor, and stability, these processes ensure that the final product is safe, appealing, and suitable for a wide range of culinary uses.
Benefits of Refined Oils for Health-Conscious Consumers
Refined oils offer several benefits that make them an appealing choice for health-conscious consumers. Understanding these advantages can help individuals make informed decisions about the oils they use in their cooking and food preparation. Here are some key benefits of refined oils:
1. Improved Flavor and Aroma: Refined oils undergo processes such as bleaching and deodorization, which remove impurities and undesirable flavors. This results in a neutral taste and aroma, making refined oils versatile for various culinary applications without overpowering the flavors of the dishes.
2. Higher Smoke Points: Many refined oils have higher smoke points compared to unrefined oils. This means they can withstand higher cooking temperatures without breaking down or producing harmful compounds. Oils with high smoke points, such as canola and avocado oil, are ideal for frying, sautéing, and baking, allowing for a wider range of cooking techniques.
3. Longer Shelf Life: The refining process helps to stabilize oils by removing compounds that can lead to rancidity. As a result, refined oils typically have a longer shelf life than unrefined oils, making them more convenient for consumers who want to stock up on cooking essentials without worrying about spoilage.
4. Nutritional Benefits: While some nutrients may be lost during the refining process, refined oils still provide essential fatty acids necessary for a balanced diet. For instance, oils like olive oil and canola oil contain healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that can promote heart health when consumed in moderation.
5. Versatility in Cooking: Refined oils are suitable for a variety of cooking methods, including frying, roasting, and baking. Their stability and neutral flavor make them a popular choice for both everyday cooking and gourmet dishes, allowing health-conscious consumers to experiment with different recipes without compromising on taste.
6. Convenience and Accessibility: Refined oils are widely available in grocery stores and often come in larger, more economical packaging. This accessibility makes it easier for consumers to incorporate healthy oils into their cooking routines.
In summary, refined oils provide numerous benefits for health-conscious consumers, including improved flavor, higher smoke points, longer shelf life, and versatility in cooking. By choosing refined oils, individuals can enjoy the advantages of cooking with oils that enhance their meals while supporting their health and wellness goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how cooking oil is refined and the various processes involved is essential for appreciating the quality and safety of the oils we use in our kitchens.
From the extraction of raw materials to the key refinement processes of degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization, each step plays a crucial role in transforming crude oil into a product that is not only safe but also appealing for culinary use.
Refined oils offer significant benefits for health-conscious consumers, including improved flavor, higher smoke points, and longer shelf life. These characteristics make refined oils versatile and convenient for various cooking methods, allowing individuals to enjoy delicious meals while supporting their health and wellness goals.
By choosing refined oils, consumers can make informed decisions that enhance their cooking experience and contribute to a healthier lifestyle. Ultimately, understanding the refining process and the benefits of these oils empowers us to appreciate the science behind the food we prepare and consume, leading to more mindful and enjoyable culinary practices.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Cooking Oil Refining
What is the process of refining cooking oil?
The refining process involves several steps including extraction, degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization to produce safe and high-quality cooking oil.
What are the benefits of using refined oils?
Refined oils offer improved flavor, higher smoke points, longer shelf life, and versatility in cooking, making them suitable for various culinary applications.
How does the extraction of crude oil work?
Crude oil is extracted through drilling, where it is pumped from underground reservoirs. This oil is then processed to separate its components for cooking oil production.
What is the Maillard reaction, and how does it relate to cooking oil?
The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs during cooking, contributing to the browning and flavor development in foods, often enhanced by the use of cooking oils.
Are there any health risks associated with using refined oils?
While refined oils are generally safe, it is important to use them in moderation and be aware of their fatty acid profiles. Some refined oils may contain unhealthy trans fats if improperly processed.
How can I store cooking oil to ensure its longevity?
Store cooking oil in a cool, dark place, tightly sealed to prevent exposure to air and light, which can lead to degradation and spoilage.
See more
Discover plenty of easy and delicious recipes you can make at home, from hearty dinners to indulgent desserts and wholesome breakfasts.




